- 1. Setup developer environment
- 2. Code Workflow
- 3. C Library Code Layout
- 4. Python Library Code Layout
- 5. LSM Daemon Code layout.
- 6. Tests
- 7. How to contribute.
This document is assuming you already read the User Guide.
1. Setup developer environment
1.1. Grab the code
# The rest document is assuming your working folder is $HOME
# which store the git repo as "$HOME/libstoragemgmt" folder.
$ git clone https://github.com/libstorage/libstoragemgmt.git
1.2. Install build dependencies
-
RHEL/Centos/Fedora
$ sudo yum install `cat rh_rpm_dependency` -
OpenSuSE/SLES/SLED
$ sudo zypper in `cat suse_rpm_dependency` -
Debian
$ sudo apt-get install `cat deb_dependency`
1.3. Compile
# Change into root of source tree
$ cd libstoragemgmt
# Setup autotools
$ ./autogen.sh
# Configure
$ ./configure
# Build it
$ make
1.4. Run from the code tree
1.4.1. Automatic way – lsmenv
# EPEL7 is needed for perl-Config-IniFiles on RHEL/Centos 7
$ sudo yum install perl-Config-IniFiles
# or openSuSE:
# sudo zypper in perl-Config-IniFiles
# or debian:
# sudo apt-get install libconfig-inifiles-perl
# Link 'lsmenv' to $HOME/bin
# Assuming libstoragemgmt is in "$HOME" and $HOME/bin is in $PATH
# Check 'lsmenv -h' for detail usage.
$ ln -s $HOME/libstoragemgmt/tools/lsmenv $HOME/bin/
# Start lsmd daemon from code tree
# You can skip the sudo if you don't intent to run plugin in root mode.
$ sudo lsmenv lsmd
# Invoke lsmcli command
$ lsmenv sim lsmcli list --type pools
# Invoke plugin test
$ lsmenv sim plugin_test
1.4.2. Manual way
# Assuming libstoragemgmt is in "$HOME"
# Notes:
# Make sure it compiled cleanly before proceeding
#
# Make sure you don't already have libstoragememgt installed
#
# If you need to run a plugin with 'root' privledges then you
# should setup the env variables and run lsmd and lsmcli as root.
# If you setup the environment then run sudo the env variables are
# not preserved and things will fail.
#
$ cd $HOME/libstoragemgmt
# Create socket folder:
$ mkdir -p /tmp/lsm/ipc/
# Link lsmcli and plugin into lsm python binding folder
$ ln -s `pwd`/tools/lsmcli `pwd`/python_binding/lsm
$ ln -s `pwd`/plugin `pwd`/python_binding/lsm/plugin
# Link Python C extention
$ ln -s `pwd`/python_binding/lsm/.libs/*.so `pwd`/python_binding/lsm/.
# Verify that the symlinks are good by
$ ls -la $HOME/libstoragemgmt/python_binding/lsm | grep "\->"
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 tasleson tasleson 63 Feb 13 12:36 _clib.so -> /home/tasleson/libstoragemgmt/python_binding/lsm/.libs/_clib.so
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 tasleson tasleson 42 Feb 13 12:51 lsmcli -> /home/tasleson/libstoragemgmt/tools/lsmcli
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 tasleson tasleson 36 Feb 13 12:36 plugin -> /home/tasleson/libstoragemgmt/plugin
# Export LSM required environment variables
$ export LSM_UDS_PATH="/tmp/lsm/ipc/"
$ export PYTHONPATH=\
$PYTHONPATH:$HOME/libstoragemgmt/python_binding/
$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=\
$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:$HOME/libstoragemgmt/c_binding
# Run lsmd daemon
# Messages are logged to syslog
$ $HOME/libstoragemgmt/daemon/lsmd \
--confdir $HOME/libstoragemgmt/config \
--plugindir $HOME/libstoragemgmt/plugin \
--socketdir /tmp/lsm/ipc \
-v
# Make sure lsmd daemon is running
$ ps -e | grep lsm[d]
6677 ? 00:00:00 lsmd
# Run lsmcli
$ $HOME/libstoragemgmt/tools/lsmcli/lsmcli ls -u sim://
# Invoke plugin test
$ $HOME/libstoragemgmt/test/plugin_test.py
2. Code Workflow
User application(for example: lsmcli)
^
|
|
v
+------------------+-----------------------+
| |
Python API or C API
| |
+------------------------------------------+
| ^
| Initial call |
v |
Socket of LSM Daemon |
| |
| Invoke and setup |
| plugin |
| v
+-------------------> Socket of LSM plugin
^
|
|
| Storage Vendor SDK
|
v
Storage Array/RAID
The communication between client and LSM daemon/plugin is based on UNIX domain socket (default folder is /var/run/lsm/ipc/) and using JSON-RPC for protocol.
Example:
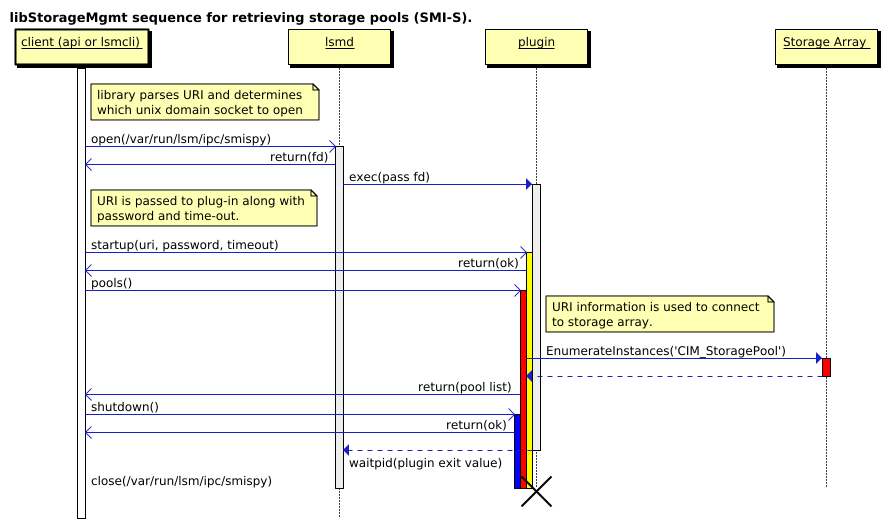
3. C Library Code Layout
The C library code is located at ‘libstoragemgmt/c_binding’ folder. It basically uses C++ codes internally for data converting between socket JSON to LSM C API.
TODO: Explain which lib we are using for JSON, socket, and etc.
3.1. Client API – libstoragemgmt/libstoragemgmt.h
The libstoragemgmt/libstoragemgmt_plug_interface.h file
is located at c_binding/include/libstoragemgmt/libstoragemgmt.h,
defining client API. It handles communication between client and plugin.
The plugin interface only accept JSON input and only provide JSON
output. This set of methods are responsible to convert C methods into
JSON format and convert plugin JSON output to C values.
Most of its methods are implemented in c_binding/lsm_mgmt.cpp.
3.2. Plugin API – libstoragemgmt/libstoragemgmt_plug_interface.h
The libstoragemgmt/libstoragemgmt_plug_interface.h file is located
at c_binding/include/libstoragemgmt/libstoragemgmt_plug_interface.h,
defining C plugin API. It handles communication between plugin and
client. It convert the output of plugin registered method to JSON
output and send back to client API.
Most of its methods are implemented in c_binding/lsm_plugin_ipc.cpp
4. Python Library Code Layout
The Python library codes are located at ‘libstoragemgmt/python_binding’ folder.
4.1. Client API and Plugin API – _client.py
The _client.py is located python_binding/lsm/_client.py defining
the client API.
Since plugin is directly communicate with client after initialisation, this file could also be treated as plugin API definition.
This is the sample code of client API user:
#!/usr/bin/python2
import lsm
lsm_cli_obj = lsm.Client("sim://") # Make connection.
pools = lsm_cli_obj.pools() # Enumerate Storage Pools.
This file is providing the lsm.Client class and its methods.
4.2. _common.py
This file is providing lsm.ErrorNumber, lsm.LsmError for public client use.
The Proxy class is for internal use, it make sure all other python exception is wrapped into LsmError.
The ‘ErrorLevel’ class is not used anywhere. Might be removed in the future.
4.3. _data.py
This file is providing LSM classes defination like lsm.System, lsm.Pool and etc.
4.4. _iplugin.py
Provide a wrapper class INetworkAttachedStorage,
IStorageAreaNetwork, and INfs to raise
LsmError.ErrorNumber.NO_SUPPORT when plugin does not implement user
requested methods.
4.5. _pluginrunner.py
Provide class PluginRunner to server in xxx_lsmplugin.
Please check libstoragemgmt/plugin/sim/sim_lsmplugin for detail.
4.6. _transport.py
Used by _client.py to provide communication between plugin and user
application.
4.7. version.py
Generated by autoconf tools for VERSION constant.
4.8. _clib.c
Python C extension to unitize libStorageMgmt C local disk API.
4.9. _local_disk.py
Provide class lsm.LocalDisk. Simply wrapping _clib.c C extension
with python exception handling.
5. LSM Daemon Code layout.
The daemon code is located at “libstoragemgmt/daemon” folder.
5.1. lsmd – lsm_daemon.c
Code workflow:
-
Scan
--plugindirargument defined folder excursively for plugins. All executable file named with_lsmpluginsuffix will be consider as a lsm plugin. -
Create a UNIX STREAM socket in
--socketdirfolder for each plugin. Example, forsim_lsmpluginplugin, and/tmp/lsm/ipcas socketdir, a UNIX STREAM socket will be created at/tmp/lsm/ipc/sim. -
Once received data on any UNIX socket, invoke the plugin binary with the socket filer description number as first argument.
-
The plugin binary will reply API request via UNIX socket.
5.2. lsm_restd
Still in experimental stage.
Using microhttpd.h for http server, json/json.h for JSON parsing,
libxml/uri.h for URI parsing.
As LSM internally use JSON data for pluing-client communication, this daemon simply convert JSON request from web service to LSM JSON format.
6. Tests
The ‘make check’ command will run three tests via runtest.sh.
6.1. C Unit Test – tester.c
Designed to test C API against simc and sim plugin.
6.2. Command Line Tool Test – cmdtest.py
Designed to test lsmcli against sim plugin.
6.3. Plugin Test(Python API) – plugin_test.py
Designed to test all plugin via Python API.
7. How to contribute.
- If it’s a new feature or big changes, discuss on the mailing list.
- Work on patches
- git format patch
- Make sure your patch meet these requirements:
- Python PEP8(python-pep8) pass.
- Python code static check(pylint): no error or fatal.
- “make distcheck” pass.
- “make rpm” pass.
- No regression for plugin_test against changed plugin.
- Every patch should leave the code tree in a working state
- WS & spelling corrections in separate patch.
- Every patch only contain one small change.
- Patch set only contain one serial change.
- Test code should be included if changed area is not tested.
- git send-email to libstoragemgmt-devel maillist.